Do I Have Pes Planus??

There are three types of flat feet: flexible flatfoot, painful rigid flatfoot, and spasmodic flatfoot. Flexible flat feet have some arch, even if the arch only appears while the person is flexing the foot or standing on their toes. Flexible flat feet may not cause pain or require treatment. Painful rigid flatfoot, on the other hand, is abnormal and causes pain, stiffness, and the inability to flex the foot. This often indicates that there is a problem with the bones in the foot, a disease is present, or an injury has occurred. Spasmodic flatfoot involves the foot being forced outward by spasmodic contractions of the peroneal muscle.
Causes
The arches of most individuals are fully developed by the age of 12 to 13. While some people are born with flat arches, for others, the arches fall over time. The tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle from above the ankle to the arch, can weaken with age and with heavy activity. The posterior tendon, main support structure for the arch, can become inflamed (tendonitis) or even tear if overloaded. For women, wearing high heels can affect the Achilles tendon and alter the structure and function of the ankle. The posterior tibial tendon may compensate for this stress and break down, causing the arches to fall. Obesity is another contributing factor, as well as a serious injury to the ankle or foot, arthritis and bad circulation such as occurs with diabetes.
Symptoms
Most people do not exhibit any symptoms of flat feet, but if the condition is due to an underlying problem, symptoms can include foot pain, mainly in the arch or heel areas, difficulty standing on tiptoes, swelling that occurs on the inside of the ankle, pain in the calf, knee, hip, or lower leg area, both feet lie flat on the ground with no gap, Shoes may not fit properly, heel may tilt away from the midline of the body more than usual, absence of foot arch when standing. If you are experiencing these symptoms and have flat feet, you should consider seeing your doctor or a podiatrist immediately for an examination.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical and foot exam will be done. Flat feet can be diagnosed by appearance. To determine if the foot is rigid, you may be asked to do some simple tasks.
pes planus treatment
Non Surgical Treatment
If your condition is bothersome, try elevating your feet and using ice on the arches to reduce swelling. Your podiatrist can recommend several orthotic aids and inserts to strengthen the tendons of your foot. He can also demonstrate stretching exercises or refer you to physical therapy to get those tendons back into shape. If the symptoms of fallen arches are painful and troubling, he may recommend a steroid injection to relieve inflammation and pain. And in some instances, he may determine that surgery is necessary.
Surgical Treatment

Procedures may include the following. Fusing foot or ankle bones together (arthrodesis). Removing bones or bony growths, also called spurs (excision). Cutting or changing the shape of the bone (osteotomy). Cleaning the tendons' protective coverings (synovectomy). Adding tendon from other parts of your body to tendons in your foot to help balance the "pull" of the tendons and form an arch (tendon transfer). Grafting bone to your foot to make the arch rise more naturally (lateral column lengthening).
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.
All The Things It Is Best To Know About Heel Serious Pain

Heel pain is most often caused by plantar fasciitis, a condition that is sometimes also called heel spur syndrome when a spur is present. Heel pain may also be due to other causes, such as a stress fracture, tendonitis, arthritis, nerve irritation, or, rarely, a cyst. Because there are several potential causes, it is important to have heel pain properly diagnosed. A foot and ankle surgeon is able to distinguish between all the possibilities and determine the underlying source of your heel pain.What Is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the band of tissue (the plantar fascia) that extends from the heel to the toes. In this condition, the fascia first becomes irritated and then inflamed, resulting in heel pain.
Causes
Near the inflamed plantar fascia attachment, but not in it, some extra bone may form, producing a small "spur". In fact, it is a shelf of bone, not a sharp spur. These "heel spurs" are commoner in people with plantar fascitis, but they can be found in people with no heel pain. The heel spur is caused by the same process as the heel pain, but the spur is not itself the cause of the pain.
Symptoms
Plantar fascia usually causes pain and stiffness on the bottom of your heel although some people have heel spurs and suffer no symptoms at all. Occasionally, heel pain is also associated with other medical disorders such as arthritis (inflammation of the joint), bursitis (inflammation of the tissues around the joint). Those who have symptoms may experience ?First step? pain (stone bruise sensation) after getting out of bed or sitting for a period of time. Pain after driving. Pain on the bottom of your heel. Deep aching pain. Pain can be worse when barefoot.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment includes resting from the activities that caused the problem, doing certain stretching exercises, using pain medication and wearing open-back shoes. Your doctor may want you to use a 3/8" or 1/2" heel insert. Stretch your Achilles tendon by leaning forward against a wall with your foot flat on the floor and heel elevated with the insert. Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications for pain and swelling. Consider placing ice on the back of the heel to reduce inflammation.
Surgical Treatment
When a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is made early, most patients respond to conservative treatment and don?t require surgical intervention. Often, when there is a secondary diagnosis contributing to your pain, such as an entrapped nerve, and you are non-responsive to conservative care, surgery may be considered. Dr. Talarico will discuss all options and which approach would be the most beneficial for your condition.
deelsonheels
Prevention

Preventing heel pain is crucial to avoid pain that can easily interrupt a busy or active lifestyle. Athletes can prevent damage by stretching the foot and calf both before and after an exercise routine. The plantar fascia ligament can be stretched by using a tennis ball or water bottle and rolling it across the bottom of the foot. With regular stretching, the stretching and flexibility of tissue through the foot can be significantly improved, helping to prevent damage and injury. Athletes should also ease into new or more difficult routines, allowing the plantar fascia and other tissue to become accustomed to the added stress and difficulty. Running up hills is also common among athletes in their routines. However, this activity should be reduced since it places an increased amount of stress on the plantar fascia and increases the risk of plantar fasciitis. Maintaining a healthy weight is also an essential heel pain prevention technique. Obesity brings additional weight and stress on the heel of the foot, causing damage and pain in the heel as well as in other areas of the foot.
Leg Length Discrepancy Treatment
Surgery is another option. In some cases the longer extremity can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the extremity. In growing children, lower extremities can also be equalized by a surgical procedure that stops the growth at one or two sites of the longer extremity, while leaving the remaining growth undisturbed. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be attained by surgically halting one or more growth centers. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the LLD will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical; the goal is to attain equal length of the extremities at skeletal maturity, usually in the mid- to late teens. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the LLD and the patient?s adult height will be less than if the shorter extremity had been lengthened. Correction of significant LLDs by this method may make a patient?s body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter legs.
Causes
Some children are born with absence or underdeveloped bones in the lower limbs e.g., congenital hemimelia. Others have a condition called hemihypertrophy that causes one side of the body to grow faster than the other. Sometimes, increased blood flow to one limb (as in a hemangioma or blood vessel tumor) stimulates growth to the limb. In other cases, injury or infection involving the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of the femur or tibia inhibits or stops altogether the growth of the bone. Fractures healing in an overlapped position, even if the epiphyseal plate is not involved, can also cause limb length discrepancy. Neuromuscular problems like polio can also cause profound discrepancies, but thankfully, uncommon. Lastly, Wilms? tumor of the kidney in a child can cause hypertrophy of the lower limb on the same side. It is therefore important in a young child with hemihypertrophy to have an abdominal ultrasound exam done to rule out Wilms? tumor. It is important to distinguish true leg length discrepancy from apparent leg length discrepancy. Apparent discrepancy is due to an instability of the hip, that allows the proximal femur to migrate proximally, or due to an adduction or abduction contracture of the hip that causes pelvic obliquity, so that one hip is higher than the other. When the patient stands, it gives the impression of leg length discrepancy, when the problem is actually in the hip.
Symptoms
The effects of a short leg depend upon the individual and the extent of discrepancy. The most common manifestation if a lateral deviation of the lumbar spine toward the short side with compensatory curves up the spine that can extend into the neck and even impacts the TMJ. Studies have shown that anterior and posterior curve abnormalities also can result.
Diagnosis
On standing examination one iliac crest may be higher/lower than the other. However a physiotherapist, osteopath or chiropractor will examine the LLD in prone or supine position and measure it, confirming the diagnosis of structural (or functional) LLD. The LLD should be measured using bony fixed points. X-Ray should be taken in a standing position. The osteopath, physiotherapist or chiropractor will look at femoral head & acetabulum, knee joints, ankle joints.
Non Surgical Treatment
To begin a path torwards a balanced foundation and reduce pain from leg length discrepancy, ask your doctor about these Functional Orthotics and procedures. Functional Orthotics have been shown to specifically reduce pain from leg length inequality, support all three arches of the foot to create a balanced foundation, maximize shock absorption, add extra propulsion, and supply more stability, enable posture correction and long-term preventive protection. Will improve prolonged effectiveness of chiropractic adjustments. Shoe or heel Lifts, Correct the deficiencies that causes imbalances in the body.

how to increase height after 18
Surgical Treatment
The bone is lengthened by surgically applying an external fixation device to the leg. The external fixator, a scaffold-like frame, is connected to the bone with wires, pins, or both. A small crack is made in the bone and the frame creates tension when the patient or family member turns its dial. This is done several times each day. The lengthening process begins approximately five to 10 days after surgery. The bone may lengthen 1 millimeter per day, or approximately 1 inch per month. Lengthening may be slower in a bone that was previously injured. It may also be slower if the leg was operated on before. Bones in patients with potential blood vessel abnormalities, such as cigarette smokers, may also need to be lengthened more slowly. The external fixator is worn until the bone is strong enough to support the patient safely. This usually takes about three months for each inch. Factors such as age, health, smoking and participation in rehabilitation can affect the amount of time needed.
Diagnosing Mortons Neuroma
 A Morton's neuroma is a benign (noncancerous) swelling along a nerve in the foot that carries sensations from the toes. The reason the nerve starts to swell is unknown. But once swelling begins, the nearby bones and ligaments put pressure on the nerve, causing more irritation and inflammation. This produces burning pain, numbness, tingling and other abnormal sensations in the toes. A Morton's neuroma also is called an interdigital neuroma, intermetatarsal neuroma or a forefoot neuroma.
A Morton's neuroma is a benign (noncancerous) swelling along a nerve in the foot that carries sensations from the toes. The reason the nerve starts to swell is unknown. But once swelling begins, the nearby bones and ligaments put pressure on the nerve, causing more irritation and inflammation. This produces burning pain, numbness, tingling and other abnormal sensations in the toes. A Morton's neuroma also is called an interdigital neuroma, intermetatarsal neuroma or a forefoot neuroma.Causes
Morton's neuroma seems to occur in response to irritation, pressure or injury to one of the nerves that lead to your toes. Factors that appear to contribute to Morton's neuroma include. High heels. Wearing high-heeled shoes or shoes that are tight or ill fitting can place extra pressure on your toes and the ball of your foot. Certain sports. Participating in high-impact athletic activities such as jogging or running may subject your feet to repetitive trauma. Sports that feature tight shoes, such as snow skiing or rock climbing, can put pressure on your toes. Foot deformities. People who have bunions, hammertoes, high arches or flatfeet are at higher risk of developing Morton's neuroma.
Symptoms
Symptoms include: pain on weight bearing, frequently after only a short time. The nature of the pain varies widely among individuals. Some people experience shooting pain affecting the contiguous halves of two toes. Others describe a feeling like having a pebble in their shoe or walking on razor blades. Burning, numbness, and paresthesia may also be experienced. Morton's neuroma lesions have been found using MRI in patients without symptoms.
Diagnosis
Your health care provider can usually diagnose this problem by examining your foot. A foot x-ray may be done to rule out bone problems. MRI or ultrasound can successfully diagnose the condition. Nerve testing (electromyography) cannot diagnose Morton neuroma. But it may be used to rule out conditions that cause similar symptoms. Blood tests may be done to check for inflammation-related conditions, including certain forms of arthritis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Once a diagnosis is obtained, it is essential to begin treatment immediately. Your podiatric physician will advise you on the most effective means. If caught early enough, good foot care, shoes that fit properly, and/or orthoses may eliminate the need for any further intervention. Other conservative measures might include oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDS), physical therapy, ultrasound or other non-invasive measures. If that doesn?t work, your podiatric physician might use injectable steroids, and/or a local anesthetic around the neuroma to reduce inflammation and pain. Many patients report relief after these measures are taken.

Surgical Treatment
The above measures are often sufficient to resolve Morton?s Neuroma. Should the condition persist or worsen despite these efforts, surgery may be recommended to remove the Neuroma. The surgery requires only a short recovery period, though permanent numbness in the affected toes can result, so such surgery is generally used as a last resort.
For Leg Length Discrepancy Chiropodists Prefer Shoe Lifts

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this problem is easily fixed, and can reduce numerous instances of lumbar pain.
Therapy for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. Most are very inexpensive, commonly costing less than twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Mid back pain is the most widespread health problem afflicting people today. Around 80 million men and women suffer from back pain at some stage in their life. It's a problem which costs employers millions of dollars each year as a result of time lost and production. New and more effective treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of lowering economical influence this condition causes.

People from all corners of the earth experience foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In a lot of these situations Shoe Lifts are usually of immense help. The lifts are capable of eliminating any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by many skilled orthopaedic physicians.
So that they can support the body in a nicely balanced fashion, the feet have got a critical task to play. Despite that, it's often the most overlooked area of the body. Many people have flat-feet meaning there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that proper posture and balance are restored.
Hammer Toes Natural Treatment
 Overview
Overview
There are two types of Hammer toe, Flexible hammertoes. If the toe still can be moved at the joint, it's a flexible hammertoe. That's good, because this is an earlier, milder form of the problem. There may be several treatment options. Rigid hammertoes. If the tendons in the toe become rigid, they press the joint out of alignment. At this stage, the toe can't be moved. It usually means that surgery is needed.
Causes
People who are born with long bones in their toes are more likely to develop hammer toe. Children who wear shoes they have outgrown may develop this condition. People who wear very narrow shoes or high-heeled shoes are also more likely to develop a hammer toe. Sometimes, pressure from a bunion can cause hammer toe. Rheumatoid arthritis is another a risk factor.
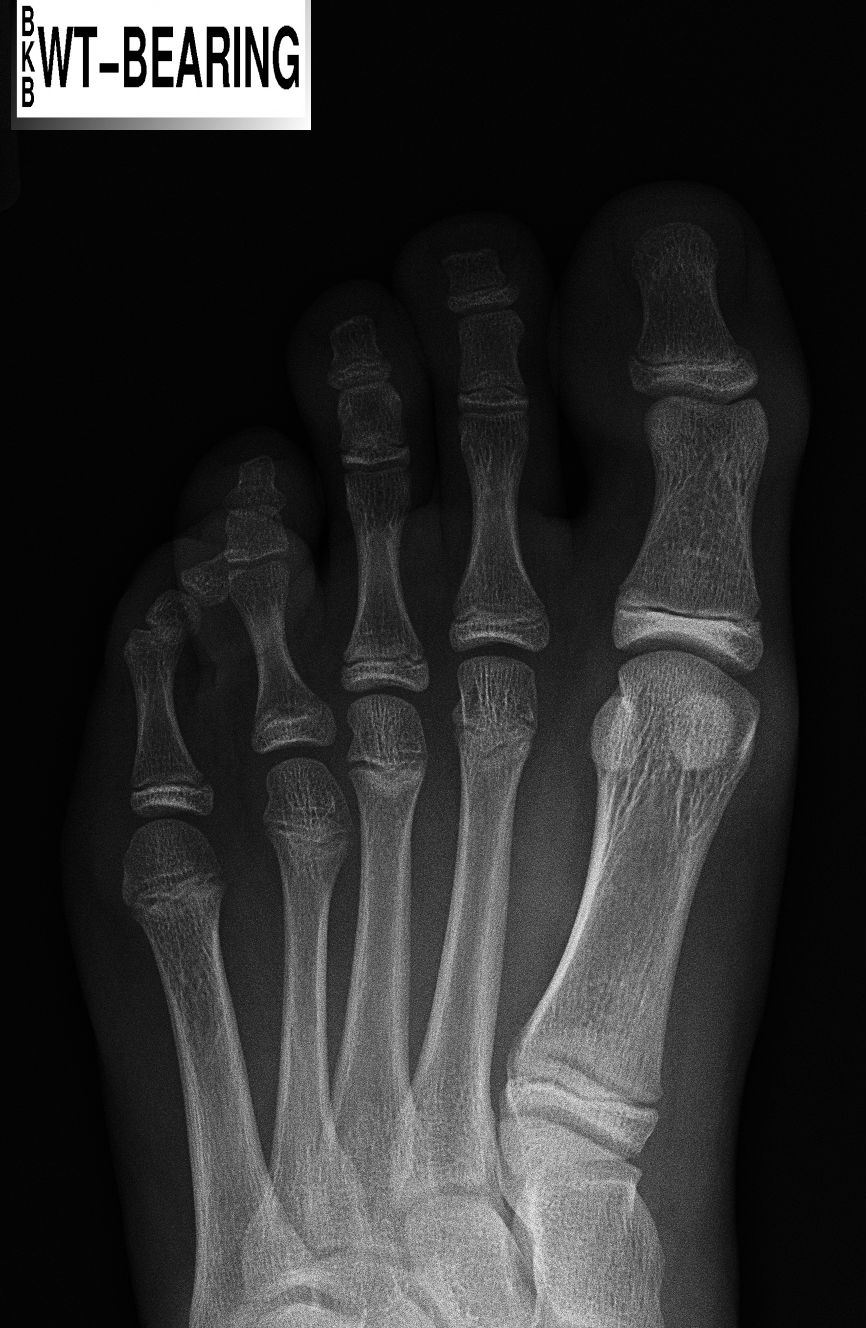 Symptoms
Symptoms
Symptoms may include pain in the affected toe or toes when you wear shoes, making it hard or painful to walk. A corn or callus on the top of the joint caused by rubbing against the shoe. Swelling and redness of the skin hammertoes over the joint. Trouble finding comfortable shoes.
Diagnosis
The earlier a hammertoe is diagnosed, the better the prognosis and treatment options. Your doctor will be able to diagnose your hammertoe with a simple examination of the foot and your footwear. He or she may take an x-ray to check the severity of the condition. You may also be asked about your symptoms, your normal daily activities, and your medical and family history.
Non Surgical Treatment
Podiatric Care may include using anti-inflammatory oral medications or an injection of medication and local anesthetic to reduce this swelling. When you go to your doctor, x-rays are usually required to evaluate the structure of your foot, check for fractures and determine the cause. The podiatrist may see you to take care of any corns that develop due to the bone deformities. They may advise you on different shoewear or prescribe a custom made orthotic to try and control the foot structure. Padding techniques may be used to straighten the toe if the deformity is flexible, or pads may be used to lessen the pressure on the area of the corn or ulcer. Your podiatric physician may also recommend a surgical procedure to actually fix the structural problem of your foot.
Surgical Treatment
A variety of anaesthetic techniques are possible. Be sure an discuss this with your surgeon during your pre-op assessment. The type of surgery performed will depend on the problem with your toes and may involve releasing or lengthening tendons, putting joints back into place, straightening a toe and changing the shape of a bone.Your surgeon may fix the toes in place with wires or tiny screws.
 Prevention
Prevention
To help prevent hammertoe, wear roomy, low-heeled shoes that allow plenty of width and length for the toes. The Mayo Clinic recommends wearing shoes that have at least 1/2 inch of space between the shoe and the longest toe.
Cause And Treating Of Hammertoes
 Overview
Overview
The 2nd toe is the most common digit to develop a Hammertoe deformity. Second toe hammer toes commonly result from an elongated 2nd metatarsal and from pressure due to an excessively abducted great toe (hallux valgus deformity) causing a bunion. Unusually long toes often develop hammer toe deformities. Painful corns often develop in hammer toe deformity, particularly of the 5th toe. Reactive adventitial bursas often develop beneath corns, which may become inflamed.
Causes
The main cause of hammer toe is poorly fitted and/or poorly designed footwear. Any footwear that is too tight in the toe box, especially high-heeled shoes, can push the toes forward, crowding one or more of them into a space that is not large enough to allow the toes to lie flat and spread as they should. Other causes include the following. Changes in foot anatomy. Sometimes the metatarsal bones in the ball of the foot can ?drop,? creating a situation in which the toes do not make contact with the surface of the shoe. The toes may then contract at one or both of the joints to re-establish contact with the surface. Traumatic injuries in which toes are jammed or broken. Diabetic neuropathy. This can cause abnormal foot biomechanics due to nerve and/or muscle damage. Damage to nerves and muscles from other conditions, such as arthritis or stroke. Heredity. 
Symptoms
Common reasons patients seek treatment for toe problems are toe pain on the knuckle. Thick toe calluses. Interference with walking/activities. Difficulty fitting shoes. Worsening toe deformity. Pain at the ball of the foot. Unsightly appearance. Toe deformities (contractures) come in varying degrees of severity, from slight to severe. The can be present in conjunction with a bunion, and develop onto a severe disfiguring foot deformity. Advanced cases, the toe can dislocate on top of the foot. Depending on your overall health, symptoms and severity of the hammer toe, the condition may be treated conservatively and/or with surgery.
Diagnosis
The earlier a hammertoe is diagnosed, the better the prognosis and treatment options. Your doctor will be able to diagnose your hammertoe with a simple examination of the foot and your footwear. He or she may take an x-ray to check the severity of the condition. You may also be asked about your symptoms, your normal daily activities, and your medical and family history.
Non Surgical Treatment
If the problem is caught in the early stages you can avoid hammer toe surgery. One of the easiest methods of treatment is to manipulate the toe out of a bent position then splint and buddy wrap it alongside it?s larger neighbour. This method of hammer toe taping will help the problem to fix itself. Make sure the toe isn?t resuming its bent shape during the recovery. To alleviate some of the painful symptoms of hammer toe avoid wearing high heels or shoes that cramp or stifle your feet. Choosing a pair of minimalist shoes can be an excellent choice for both foot and postural health. Wearing shoes that give the toes plenty of space and are comfortable lined is also a smart choice. Hammer toe recovery starts be treating the toe respectfully. Soft insoles or protection for the corn can also provide additional assistance.
Surgical Treatment
Joint resection procedures involves removing part of one of the two small joints of the toe directly underneath where the digit is crooked. The purpose is to make room for the toe to be re-positioned flat or straight. Because hammer toes become rigid or fixed with time, removing the joint becomes the only option when the knuckle is stiff. Its important to understand that this procedure does not involve the joint of the ball of the foot, rather the a small joint of the toe. Medical terminology for this procedure is called a proximal interphalangeal joint arthroplasty or a distal interphalangeal joint arthroplasty, with the latter involving the joint closer to the tip of the toe. 
Prevention
You can avoid many foot, heel and ankle problems with shoes that fit properly. See your doctor if you have foot pain that's persistent and that affects your ability to walk properly and carry out other motions with your foot. Also, see your doctor if one or more of your toes has developed a clenched or claw-like appearance.